
A) Offshore Oil Spill Management:
Oil Spill Management in ONGC is of utmost importance as Oil spills can cause severe damage to marine ecosystems which includes marine life and coastal habitats. By implementing effective oil spill management practices, ONGC aims to minimize the adverse impacts of oil spills, prevent contamination of water bodies, preserve fragile ecosystems and work towards sustainable and responsible operations. The key aspects of oil spill management in ONGC includes:-
- Prevention: ONGC focuses on preventive measures to minimize the risk of oil spills. All the Offshore Installations and Pipelines are designed as per International Standards i.e. API, ISO, IMO etc. which have all the safety systems inbuilt at the design stage. In addition, regular inspection and maintenance of equipment, pipelines and offshore structures are carried out as per maintenance protocol. The trunk pipelines are having adequate safety mechanism like Safety Shut Down valves and subsea isolation valves to minimize the effect due to loss of containment in pipelines. All offshore wells are fitted with Sub surface safety valve (SSSV) and Surface Safety valves (SSV) which can be remotely operated from Control Room in case of emergency situations in Well Head Platforms. All the offshore installations are equipped with oil & gas detectors and fire suppression systems. In the event of emergency, the offshore installations can be shut down with the emergency shutdown systems. Thus, ONGC is fully equipped to handle any emergency in its offshore operations and adheres to strict safety standards and practices to prevent accidents and operational failures that can lead to oil spills.
- Spill Response: Indian Coast Guard is the Central Coordinating Authority in India for matters related to Oil Spill. National Oil Spill Disaster Contingency Plan (NOSDCP) promulgated by Indian Coast Guard (ICG) is the apex plan for responding to oil spill disasters in Indian waters and is applicable to shipping, ports, and oil industries. As per NOSDCP, Oil pollution preparedness and response requirements are categorized into three ‘tiers’ i.e. Tier 1, Tier 2 & Tier 3. The tiered approach to oil contingency planning identifies resources for responding to spills of increasing magnitude and complexity.
| Requirements | ONGC status | |
|---|---|---|
| Tier 1 | It is concerned with preparedness and immediate response to a most mild spill within the capabilities of facility operator, usually near the company's own facilities eg. Offshore Installations, SBMs, harbours, etc. ( upto 700 tons of oil spillage) | ONGC has its own Tier -1 facility onboard Multi Support Vessels (MSVs) for combating oil spills in its operational area as per NOSDCP requirements. |
| Tier 2 | It is concerned with preparedness and response to a spill that requires the co-ordination of more than one source of equipment and personnel, larger than a Tier 1 spill, but is still in the area of the producing company's facilities. ( 700 to 10,000 tons) | Indian Coast Guard (ICG) is the nodal agency. ONGC will activate Regional Contingency Plan (RCP), West. |
| Tier 3 | It is concerned with a major spill requiring the mobilization of all available national and International resources. Global responses necessary due to scale, impact and complexity of spill. (more than 10,000 tons) | ONGC is maintaining Participant Membership of Oil Spill Response Limited (OSRL), UK which is an expert agency in combating major oil spills. |
In the event of an oil spill, ONGC will activate Oil Spill Contingency Plan and take immediate action to contain and control the spill as per the response strategy. This involves either deploying appropriate containment booms, skimmers, and other specialized equipment to minimize the spread of oil and facilitate its recovery or dispersant spraying through Vessels.
Tier-1 Oil Spill Response Facility
ONGC is maintaining following Tier -1 oil spill response resources onboard its 7 Multi-Support Vessels (MSVs) as per the requirements of NOSDCP:-
- 3000 meters Inflatable oil containment boom with 6 power pack
- 8 nos. skimmer (Brush type & Multi Skimmer)
- 10 nos. inflatable storage bags of 5000 ltr. Capacity each
- 14 nos. oil spill dispersant spray unit
- 15 m3 of Oil Spill Dispersant
- For Shoreline oil spill response expert external agency is hired
Apart from above, ONGC is also funding Tier-1 Oil spill response facility and services in Mumbai Harbour under an MOU signed between Mumbai Port Trust, Jawaharlal Nehru Port Trust and other oil companies (IOCL, BPCL, HPCL, RIL etc.). This facility is for combating oil spill in Mumbai and JNPT port trust area which also covers ONGC’s Nhava Supply Base and Uran Plant.
In case of escalation of Tier-1 to Tier-2 level, ONGC will activate RCP (West) and will continue to combat the oil spill under the command and control of Indian Coast Guard and Indian Navy. Further escalation of Tier-2 to Tier-3 level, ONGC will seek the services of Oil Spill Response Limited, UK to coordinate response efforts and ensure a swift and effective response.
- Preparedness: ONGC has robust oil spill contingency plans and emergency response procedures in place to effectively respond to oil spills if they occur. ONGC has developed Oil Spill Contingency Plan (OSCP) for both the Coasts. The contingency plan has been developed as per the NOSDCP guidelines. Some of the important features of OSCP includes:-
- Roles and responsibilities of the key persons involved in oil spill management
- Organogram of oil spill Control for Tier-1, Tier-2 & Tier-3 scenarios
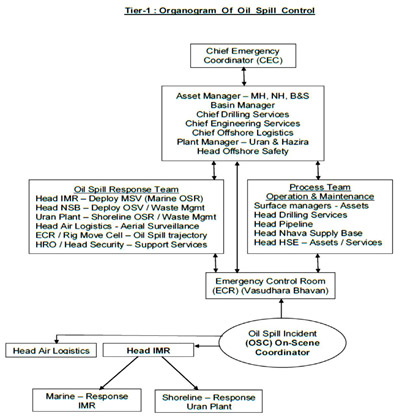
-
- Risk Assessment for predicting the possible and worst case scenarios
- Oil spill modelling studies through Hydrodyn-OILSOFT software developed by Environ Software Pvt. Ltd., Bangalore for predicting the fate and oil spill trajectory for various conditions. The oil spill trajectory due to continuous oil spill of 60m3/hr in MH field during Monsoon season (July 2018) is depicted below:-
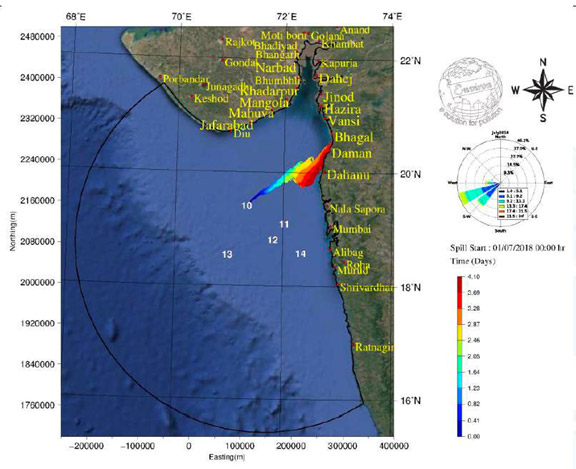
-
- Response Strategy
- Environmental Sensitivity Index Mapping for coastal area
- Net Environmental Benefit Analysis (NEBA) studies to evaluate and compare oil spill response options.
- Interface with Regional Contingency Plan of Naval Command and National Oil Spill Disaster Contingency Plan (NOSDCP) of Indian Coast Guard.
As a part of Preparedness, ONGC also conducts regular internal mock drills and exercises and IMO level trainings to train its staff and equip them with the necessary skills and knowledge to respond promptly and efficiently to spills. For the year 2022-23, a total of 159 oil spill mock drills were carried out involving ONGC Offshore Platforms, Offshore Drilling Rigs and Vessels and MSVs. ONGC is also training it manpower in IMO Level – 1, 2 & 3 trainings which are designed for First Responders, On-scene Coordinators and Oil Spill Managers respectively. A total of 53 ONGC personnel and 37 contractual personnel are trained in IMO level trainings.
As a part to stakeholder engagement, ONGC also participates in External Mock drills with Indian Navy and Indian Coast Guard. Exercise Prasthan by Indian Navy was conducted at one of the ONGC offshore platform in April 2023 to validate measures and procedures to address contingencies such as oil spill, fire, man overboard that may occur in offshore installations. ONGC also participated in National Level Pollution Response Exercise (NATPOLREX-VIII) conducted by Indian Coast Guard in April 2022 off Mormugao harbour, Goa to enhance the preparedness and response capability of all the stakeholders in combating marine oil spills under National Oil Spill Disaster Contingency Plan (NOSDCP).

- Monitoring and Assessment: ONGC closely monitors its operations, including pipelines, offshore Installations, offshore drilling platforms to detect any signs of spills or leaks. Standard Operating Procedures for offshore hydrocarbon pipelines includes procedure for flow monitoring system, external acoustic inspection, maintenance pigging and Internal Corrosion monitoring. Ongoing monitoring and assessment help in identifying areas for improvement and implementing necessary measures to prevent oil spills.
ONGC has been undertaking Offshore Environment Monitoring of Western Offshore through credible organisations since 1994 and in the Eastern Offshore since 2014. Until 2011 it had been done through National Institute of Oceanography (NIO), Goa and there after NABL accredited private agencies (M/s Detox Corporation Pvt. Ltd., Surat and M/s Vimta Labs Ltd., Hyderabad). In all the study reports, no instances of oil spill had been reported by any of the three agencies which is in consonance with Indian Coast Guard records. All reports have also indicated that the offshore marine environment has not been affected by ONGC’s operations.
- Compliance and Reporting: ONGC complies with all applicable environmental regulations and reporting requirements related to oil spill management. Annual Returns are being submitted yearly to Indian Coast Guard. Joint Inspection of Tier-1 oil spill response facility of ONGC is being carried out by Coast Guard and Oil Industry Safety Directorate (OISD) every year.
Overall, oil spill management is vital for ONGC to protect the environment, maintain a positive reputation, comply with regulations, ensure worker safety, minimize financial risks, and engage effectively with stakeholders.
B) Onshore Oil Spill Management:
Oil spills in onshore operations may occur due to leakage from pipelines (trunk lines, flow lines etc.) originating from well site/ production installations; storage tanks at production installations/ plants and during transportation of crude oil through tankers.
ONGC is having a centralized contract with its joint-venture company ONGC TERI Biotech Limited (OTBL) to take care of the restoration of oil spill sites and further bio-remediation of oil contaminated soil. Land restoration is usually completed within 10-15 days of the spill as per the contract and include following activities:
- Cleaning up of oil spill area
- Lifting of Oily Slush/ recovery of Oil
- Excavation of Oil contaminated soil
- Transportation of Oil contaminated soil / Oily slush
- Re-filling of Excavated Oil contaminated Soil with Fresh Native Soil
After land restoration, bio-remediation of Oil Contaminated soil is undertaken in specially designed pits in ONGC installations. It is ensured that the Total Petroleum Hydrocarbon (TPH) of the treated oil contaminated soil is less than 0.5% (5000 ppm) in consonance with the Hazardous and Other Wastes (Management and Trans-boundary Movement) Rules, 2016.
OTBL are having offices and dedicated team of technical manpower spread across various Assets of ONGC such as Ahmedabad, Mehsana, Jorhat and Nazira for immediate start of restoration job once an oil spillage is reported. Further, ONGC is having well-defined SOP for Management of Oily Waste to take care of onland oil spillages.
During the last three financial years, 1,74,324 MT of Oil Contaminated Soil has been bio-remediated in ONGC.


